In the digital era, chat applications have revolutionized communication, bringing people together across distances. A well-designed chat system is crucial for seamless user experiences. In this blog, we delve into the intricate world of chat system design, covering aspects such as user management, real-time messaging, media sharing, and ensuring system scalability.
 |
| system design for chat application |
Requirements
Functional Requirements
Functional requirements define what a system or software application should do to meet the needs of its users.Here are the functional requirements for a chat-based system:
- User Data Management
- One-to-One Chat
- Group Messaging
- Media Sharing
- Message Status
Non-Functional Requirements
Non-functional requirements specify the qualities or attributes of a system rather than its specific features. Here are some :
- low latency
- high reliability
- high availability
- scalable & efficient
Capacity
Capacity refers to the maximum capability or resources that a system or infrastructure can handle or accommodate. It indicates the limit or threshold at which the system can effectively perform its intended functions.
Now, Let us assume following parameters per day,
Now, Let us assume following parameters per day,
- 100 million active users: This is the number of users actively using the chat system.
- Each user sends 20 messages: This means each user sends 20 messages within a given time period.
- Total messages sent by 100 million users: 100 million users * 20 messages = 2 billion messages. Each user shares 5 media files: This assumes that each user shares 5 media files, such as images or videos.
- Size of each media file: 50 KB (kilobytes) Total size of media shared by 100 million users: 100 million users * 5 media * 50 KB = 25 terabytes (TB).
High Level Design
In high level design ,we also have data model design in which we design database schema for our system by considering functional requirements. But we already have done that in one of our blog. Here is link in which we design schema for social media application.
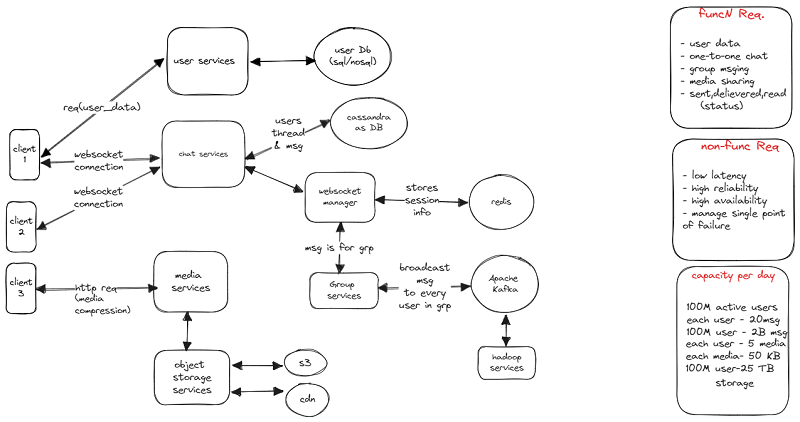
User Management
In a high-level design, user management involves the process of handling user-related operations within a system. It typically includes user authentication, authorization, and user data management. In this scenario, the user services component acts as an interface for requesting user data from its own database, which can be either SQL or NoSQL based on the specific requirements.
The user services module handles user-related functionalities, ensuring secure access to user data and efficient retrieval of user information when requested by other components or services within the system.
One-to-One messaging
 |
| one-to-one messaging |
In the one-to-one messaging, the process begins with the client initiating a WebSocket connection with the server. This WebSocket connection allows bidirectional and persistent communication between the client and the server.
(more on it read here)
To efficiently handle session and request information for different users, Redis is used as an in-memory distributed cache service. Redis stores user and server information, allowing quick access to relevant data. When a message is sent, Redis helps identify the recipient user and the server to which the sender's client is mapped. It facilitates the communication between the server and the recipient client.
In parallel, the message itself is stored in a database. In this case, Cassandra is used as the database system. Cassandra offers various functionalities that contribute to system scalability, and it supports database sharding. By using Cassandra, the system can handle a large volume of messages and efficiently store and retrieve them.
Group messaging
 |
| group messaging |
In the case of group messaging, when a client sends a message intended for a group, the message is received by the chat services component. The chat services component then forwards the request to the WebSocket manager.
The WebSocket manager, in turn, interacts with Redis to update the timestamp of the user and retrieves the user IDs associated with the particular group ID. To handle group-related operations and information, a separate component called the group services is involved. The group services component is connected to Apache Kafka.
Apache Kafka plays a crucial role in decoupling the services and ensuring a more scalable and resilient architecture. It helps to streamline the communication flow and prevents dependencies and complexities that could arise from a tightly coupled system.
Once the group services component retrieves the user IDs from Redis for the specified group, it uses Kafka to broadcast the message to all the user IDs in that group. This ensures that the message is efficiently distributed to all the intended recipients in the group.
Media sharing
 |
| media sharing |
In the case of media sharing, when a user wants to share media with another user, the media needs to be compressed for quick transfer and retrieval. The media is then shared with the media service component, which is responsible for storing the media in a separate service.
For storing and managing media files, an object storage system such as Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service) is commonly used. Object storage breaks down the media into objects, which are then stored in a distributed and scalable manner across the storage infrastructure.
To ensure efficient delivery of media to users, a Content Delivery Network (CDN) is employed. A CDN helps distribute the media files across multiple network systems, geographically closer to the users. This reduces latency and improves the overall performance of media delivery.
By utilizing object storage like S3 and leveraging a CDN, the media service component can efficiently handle the storage, retrieval, and distribution of media files, ensuring a seamless media sharing experience for users.
Message Status
 |
| msg-status flow |
In the context of message status in a chat system, here is a breakdown of the flow:
Sent Message: When a client sends a message to another client (client-2), the message data is first received by the server to which client-1 is mapped. The server then saves the message data to the database for storage. Once the message is successfully saved, a response is sent back from the server to client-1 indicating that the message has been sent.
Delivered Message: To determine if a message has been delivered to client-2, the chat-services component comes into play. The server to which client-1 is mapped sends the message to the server associated with client-2 through chat-services. If client-2 is connected to the network and available, the message is delivered to client-2. Additionally, an acknowledgment is sent back from client-2 to client-1, indicating that the message has been delivered.
Read Message: When client-2 opens the chat application and creates a WebSocket connection with the server, a connection is established between client-1 and client-2. At this point, if client-2 reads the message sent by client-1, an acknowledgment is sent from client-2 to client-1, indicating that the message has been read.
Making system efficient
Now, to address the non-functional requirements in the existing system, here are some approaches:
API Gateway: By implementing an API gateway, you can efficiently manage multiple protocols and interactions with various services. The API gateway acts as a centralized entry point, routing incoming requests to the appropriate services based on the request's characteristics. This helps in achieving better control, security, and scalability.
Load Balancing: Adding a load balancer after the API gateway helps distribute the incoming traffic among multiple servers. Load balancing optimizes resource utilization, improves system performance, and reduces response times. It ensures that no single server becomes a bottleneck and helps achieve high availability by redirecting requests to healthy servers if one server fails.
Load Balancer for Chat Services: Given that chat services often experience high loads and require real-time communication, adding a load balancer specifically for chat services can further enhance performance and scalability. This load balancer can distribute incoming chat requests across multiple chat servers, ensuring efficient handling of chat messages and maintaining responsiveness.
 |
| update system design |
In conclusion, designing a chat-based system involves considering various functional and non-functional requirements. Key components such as user management, messaging, media sharing, and message status tracking need to be carefully designed and integrated. By utilizing technologies like websockets, Redis, Cassandra, and API gateways, we can achieve low latency, high reliability, and scalability. Load balancers play a crucial role in distributing traffic and avoiding single points of failure. Overall, a well-designed system ensures efficient communication, seamless user experience, and effective management of chat-based applications.



0 Comments